The debate between omnivorous and vegan diets has gained significant attention, with advocates on both sides claiming superior health benefits. While some argue that including meat provides essential nutrients, others believe a plant-based diet is the key to longevity and heart health. But which diet truly offers the best overall benefits? Let’s explore the differences, advantages, and potential drawbacks of each approach.
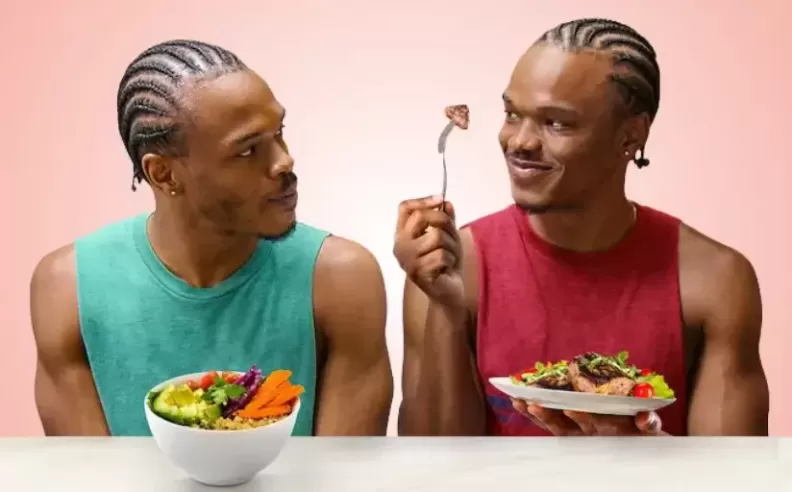
A recent study on identical twins compared the impacts of an omnivorous diet versus a strictly vegan lifestyle. Both groups experienced weight loss, but those following a vegan diet showed greater improvements in heart health, particularly in lowering bad cholesterol levels.
However, the study also highlighted some downsides to a plant-based diet. Vegan participants found it harder to gain muscle mass, had lower vitamin B12 levels, and reported lower overall satisfaction with their diet. While the findings provide valuable insights, the study’s small sample size and short duration make it difficult to draw absolute conclusions.

An omnivorous diet does not have to mean an excessive intake of processed foods or unhealthy fats. A well-balanced omnivorous approach includes lean meats, fish, vegetables, whole grains, and legumes.
The Mediterranean diet is a prime example, incorporating fish, nuts, and olive oil while limiting red meat intake. This dietary pattern has been associated with improved heart health, lower cholesterol, and overall longevity.

Not all vegan diets are created equal. While a diet rich in whole foods such as legumes, whole grains, vegetables, and nuts provides significant health benefits, relying on processed vegan products can lead to nutrient deficiencies and imbalanced nutrition.
To thrive on a vegan diet, individuals must ensure adequate protein intake from sources like tofu, lentils, and quinoa. Additionally, supplementation for vitamin B12, iron, and omega-3 fatty acids may be necessary to maintain optimal health.
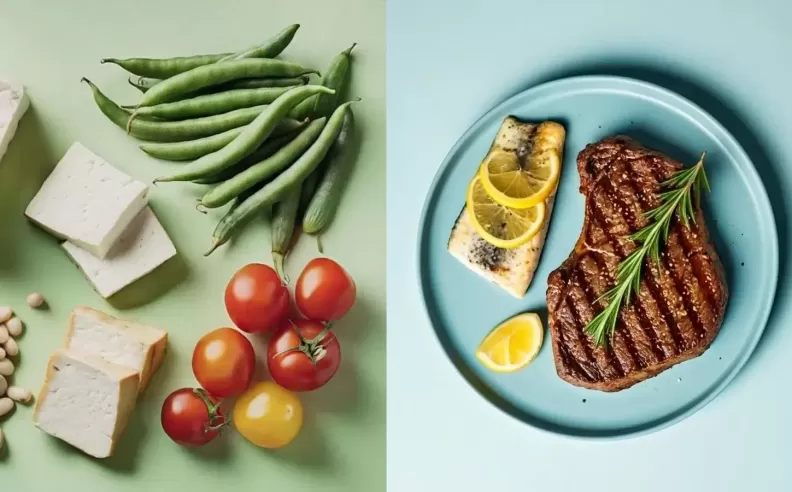

Omnivorous diets typically provide high-quality proteins that are easily absorbed, along with essential nutrients like vitamin B12, zinc, and omega-3 fatty acids. However, if not managed well, they can also lead to increased saturated fat and cholesterol consumption.
On the other hand, vegan diets offer higher fiber intake and are rich in antioxidants, vitamins A, C, and E, and essential minerals like magnesium. Despite these benefits, plant-based diets may lead to deficiencies in vitamin B12, vitamin D, and iron, requiring supplementation to maintain overall well-being.

There is no definitive answer to whether an omnivore or vegan diet is superior both have their advantages and challenges. The best approach depends on individual health goals, lifestyle, and nutritional preferences.
For those seeking heart health benefits and weight management, a well-planned vegan diet may be ideal. Meanwhile, individuals looking for balanced muscle growth and nutrient diversity may benefit from an omnivorous approach.
Ultimately, a flexible diet that prioritizes whole, unprocessed foods whether plant-based or omnivorous can provide the best of both worlds and promote long-term health.

Started my career in Automotive Journalism in 2015. Even though I'm a pharmacist, hanging around cars all the time has created a passion for the automotive industry since day 1.

