Male pattern baldness is a common issue that affects men of all ages, often starting before the age of 21. For many, losing hair can be a distressing experience, leading to questions about why it happens and what can be done to slow or prevent it. Whether caused by genetics, age, or other factors, baldness can be managed with the right treatments. This article explores the causes of male baldness, treatment options, and ways to reduce hair loss.
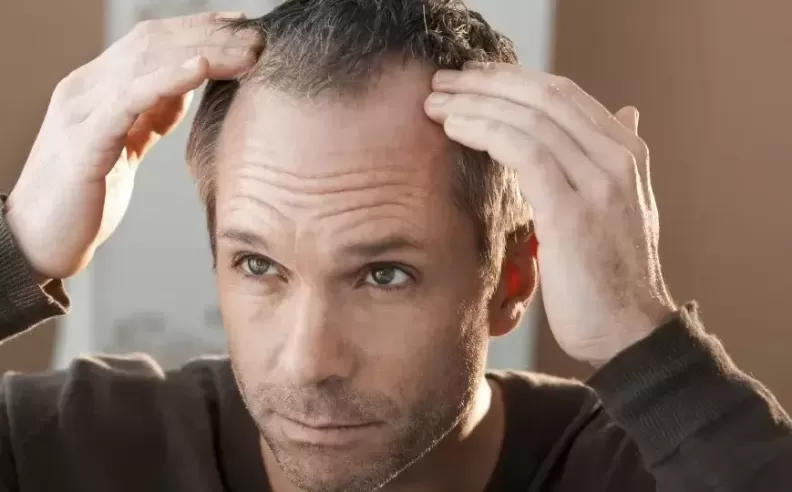

Most men experience baldness due to a hereditary condition called androgenetic alopecia, or male pattern baldness. According to the American Hair Loss Association, 95% of hair loss cases in men stem from this genetic trait. The condition is triggered by a sensitivity to dihydrotestosterone (DHT), a byproduct of testosterone. Over time, hair follicles sensitive to DHT shrink, shortening the lifespan of each hair. Eventually, the follicles stop producing hair altogether, leading to the typical receding hairline and thinning crown that characterize male pattern baldness.
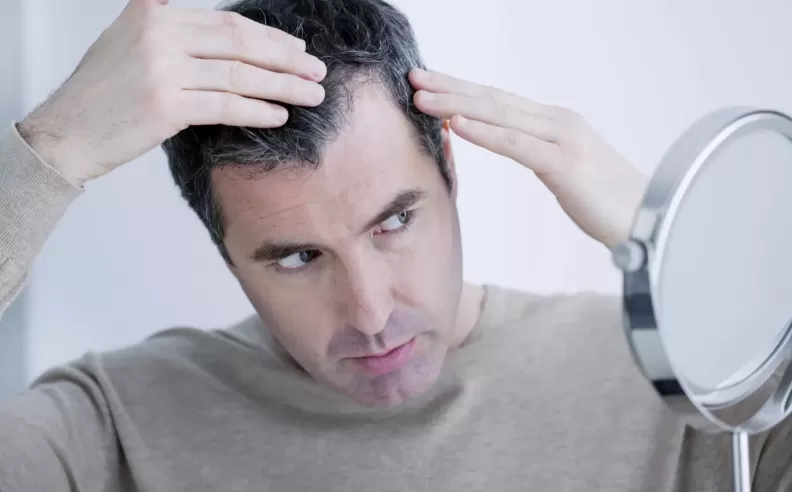

Male pattern baldness can begin early, with approximately 25% of men showing signs of hair loss before the age of 21. By the age of 35, about 66% of men experience noticeable thinning, and by 50, roughly 85% have significantly thinner hair. Age accelerates the effects of DHT on hair follicles, making it more likely for men to lose hair as they grow older.

While male pattern baldness is the most common cause, other conditions can lead to hair loss as well. These include alopecia areata, an autoimmune disorder where the immune system attacks healthy hair follicles, leading to patches of hair loss. Another condition, telogen effluvium, can result from physical or emotional stress, causing hair to shed excessively. Nutritional deficiencies, particularly in iron and vitamins, can also cause hair to fall out, while some medications, including chemotherapy drugs and certain antidepressants, can lead to temporary hair loss.
Several treatment options are available to slow or manage hair loss. Medications such as finasteride and minoxidil are commonly prescribed to prevent further hair thinning. Finasteride is a prescription pill that blocks DHT, while minoxidil is a topical treatment that promotes hair growth. Both treatments may take at least six months to show results. For more advanced cases, laser therapy and hair transplant surgery offer alternatives. Laser treatments help stimulate hair follicles, while transplant surgery moves healthy hair follicles to thinning areas, providing a permanent solution for hair restoration.

Although it is difficult to fully reverse male pattern baldness, certain measures can help slow hair loss. Using treatments like finasteride and minoxidil at the first signs of thinning can prevent further hair loss. Additionally, maintaining a healthy lifestyle by eating a well-balanced diet, managing stress, and quitting smoking can improve overall hair health. Regular scalp massages may also stimulate hair growth by improving circulation. However, once medications are discontinued, hair loss may resume, making it essential to consult a doctor for a long-term treatment plan.

Started my career in Automotive Journalism in 2015. Even though I'm a pharmacist, hanging around cars all the time has created a passion for the automotive industry since day 1.

